When Writing About Childhood Trauma In A Novel, It's Important To Handle The Topic With Sensitivity And
When writing about childhood trauma in a novel, it's important to handle the topic with sensitivity and nuance. Here are some quick tips to consider:
1. Research and understand: Take the time to research and understand the specific type of trauma you're addressing in your novel. This will help you portray it accurately and respectfully.
2. Show the impact: Explore how the childhood trauma has shaped the character's thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. Illustrate the long-lasting effects it has had on their development and relationships.
3. Use flashbacks sparingly: Utilize flashbacks strategically to reveal key moments from the character's past that contribute to their trauma. Ensure that the flashbacks serve a purpose in the narrative and provide deeper insights into the character's experiences.
4. Depict coping mechanisms: Show how the character has developed coping mechanisms to deal with their trauma. This can include avoidance, dissociation, or seeking control in certain areas of their life.
5. Allow for healing and growth: Give your character opportunities for healing and growth throughout the story. Show how they confront their trauma, seek support, and gradually find ways to overcome the impact it has had on their life.
6. Avoid sensationalism: Handle the portrayal of childhood trauma with care, avoiding excessive graphic or gratuitous details. Focus on the emotional journey of the character rather than relying solely on shocking events for impact.
7. Show support systems: Include supportive relationships and resources that aid the character in their healing process. This can involve therapists, friends, or mentors who offer understanding, guidance, and empathy.
8. Highlight resilience: Illustrate the character's strength and resilience in the face of their trauma. Show how they find ways to persevere, grow, and rebuild their lives despite the challenges they have faced.
9. Offer hope and redemption: Provide a sense of hope and the possibility of healing for your character. Allow them to find moments of redemption and transformation, demonstrating that healing is attainable.
10. Approach with empathy: Approach the topic of childhood trauma with empathy and compassion. Treat the characters' experiences with respect, acknowledging the complexity and individuality of each person's journey.
More Posts from Aemondcito and Others
George R R Martin is an American novelist and short story writer, screenwriter, and television producer. He is the author of the series of epic fantasy novels A Song of Ice and Fire, which was adapted into the Emmy Award-winning HBO series Game of Thrones (2011–2019).
01 - The human heart in conflict with itself is the only thing worth writing about. You need characters to question who, and what, they are and how they fit within the world around them. This is key for character development.
02 - Write for yourself. Following trends, or pleasing your audience in spite of your own plans, harms good storytelling. Listening to critique is good, but inevitably you must be entertained and feel your way through the writing process.
03 - Anyone can die, and death is a key part of any story with conflict. Don't give your characters any special treatment, have them play by the same rules you set upon your world. Not only does it add constant tension, but it also creates a realistic atmosphere.
04 - Sometimes an idea can just come to you. If so, do not disregard it, instead follow the idea as a writer and write it! It could either lead into an interesting project or serve as useful practice.
05 - Show don’t tell. Immersion is essential to any story. Only through visuals and vivid descriptions of your world, can your audience even start to imagine themselves in your world.
06 - Allow yourself to discover in the process of writing. While you need to know the major outcomes of the story, and character arcs, allow yourself to enjoy and be aware of your sixth sense on your way through the story.
07 - When writing a script, dialogue should never be too long. Other than a few monologues, or moments, keep it short and sweet. Also, read the dialogue aloud by yourself or with the cast, this is a simple effective way to see if it works.
08 - When adapting a novel, you’ll always lose some content. However, a good adaptation rides the fine line between cutting side content and keeping smaller meaningful moments that enrich the story.
09 - Being a writer is not a career for those who wish to be stable. It is a massive risk in every way. A true writer, even during the lows of their career, will never stop storytelling. It is essential to whom they are. So, from a beginner to a bestseller, never stop writing.
10 - The ending to an act is fundamental to keeping the audience engaged with your story. Leaving it on a cliff-hanger, or teasing the audience with a different outcome can be the best way to break up converging storylines and finished acts.
How to write a negative character arc
Here’s the simplest way to break down the building blocks of a negative character arc in your novel!
Here’s the A-Z on negative character arcs
It’s totally possible to pull off a negative character development, for ANY person in your story, whether that’s a side-character, villain, or the protagonist.
Here’s something no one tells you, but it’s actually fundamentally simple.
You can do this with a very easy formula. Typically, a positive arc means that you set out with one main character flaw/issue, which that character overcomes by the end of the story.
So all you need is:
a flaw your character NEEDS to overcome
a goal they WANT to achieve
For a positive arc, they’d succeed at their NEED. Then maybe their WANT as well. For a negative, they simply never fulfil their NEED.
This means they never overcome the flaw they are supposed to face. In fact, they ignore it so confidently, it becomes a PROBLEM. They will never truthfully own up to their mistakes.
This is where you can let it get worse, let it develop into fatal flaw, and let more issues arise from it. As for their WANT? They’ll usually put their external goal above everything else, and dig themselves even deeper into personal disarray, where they won’t recognize themselves any longer.
If you need a hand getting started on your novel, we have 3 coaches at The Plottery who can work with you intensively for 4 month to skill up your writing and help you finish your first draft.
Apply through the [link here] or below!

Different Ways to Describe Brown Eyes
-> feel free to edit and adjust pronouns as you see fit.
Her eyes were the color of honey, irises swirling like the sweet nectar.
His eyes—the color of an intoxicating champagne—beckoned her over with nothing more than a wink and a smile.
They had eyes like mud, perfectly matched with the frown that permanently stained their face.
Her eyes were as bright as the raging sun and the color of dancing flames.
They wore blue eyeshadow to contrast their dark brown eyes.
Her eyes were as beautiful as the leaves of trees in autumn.
His eyes were nearly black, like a void that held a lifetime of secrets.
Dirt. She had eyes like dirt. They were almost as dirty as her personality.
Their eyes reminded her of old brick libraries and vintage books.
She had the kind of eyes that made thieves wonder why they bothered to steal pieces of art.
His eyes made her think of the sandcastles she used to build as a kid.
Their eyes were the same color as the old oak tree their great-great-grandfather planted in the backyard.
His eyes were the same color as the bottle of liquor in his hand.
They had a smile like spring, but their eyes were autumn with a hint of passing summer.
Her dark eyes were flaked with gold.
His brown eyes had tragedy weaved behind his irises.
Brown, copper eyes that paired with the dry blood stuck to their face watched him as he stalked across the tiled floor.
Tips for creative writers:
1. Read widely: Read books, articles, and poetry across different genres and styles. This exposure to diverse writing will expand your vocabulary, inspire new ideas, and help you develop your own unique voice.
2. Write regularly: Establish a writing routine and stick to it. Set aside dedicated time each day or week to write, even if it's just for a short period. Regular practice is key to honing your skills and maintaining creative momentum.
3. Embrace creativity exercises: Engage in writing exercises or prompts to stimulate your imagination. Explore free writing, brainstorming, or visual prompts to spark new ideas and challenge your creative boundaries.
4. Edit and revise: Don't be afraid to revise your work. Editing is a crucial part of the writing process, allowing you to refine your ideas, improve clarity, and enhance the overall quality of your writing. Embrace feedback and be open to making changes.
5. Develop unique characters: Create well-rounded and believable characters by giving them depth, flaws, and distinctive voices. Explore their motivations, desires, and conflicts to make them relatable and engaging for readers.
6. Show, don't tell: Instead of telling readers what is happening or how characters feel, strive to show it through vivid descriptions, sensory details, and compelling dialogue. Engage the readers' senses and immerse them in your storytelling.
7. Pay attention to pacing: Balance the pace of your writing to maintain reader engagement. Mix moments of tension and action with quieter, reflective scenes. Vary sentence length and structure to create rhythm and keep the narrative flowing.
8. Create compelling dialogue: Craft dialogue that is realistic, purposeful, and reveals character traits. Use dialogue to advance the plot, reveal conflicts, and deepen relationships between characters.
9. Embrace constructive feedback: Seek feedback from trusted peers, writing groups, or mentors. Constructive criticism can help you identify blind spots, refine your writing, and grow as a writer.
10. Stay inspired and curious: Maintain a sense of curiosity about the world around you. Seek inspiration from art, music, nature, and everyday experiences. Keep a journal to capture ideas, observations, and inspiration that may fuel your writing.
Happy writing!
So my problem with most ‘get to know your character’ questioneers is that they’re full of questions that just aren’t that important (what color eyes do they have) too hard to answer right away (what is their greatest fear) or are just impossible to answer (what is their favorite movie.) Like no one has one single favorite movie. And even if they do the answer changes.
If I’m doing this exercise, I want 7-10 questions to get the character feeling real in my head. So I thought I’d share the ones that get me (and my students) good results:
What is the character’s go-to drink order? (this one gets into how do they like to be publicly perceived, because there is always some level of theatricality to ordering drinks at a bar/resturant)
What is their grooming routine? (how do they treat themselves in private)
What was their most expensive purchase/where does their disposable income go? (Gets you thinking about socio-economic class, values, and how they spend their leisure time)
Do they have any scars or tattoos? (good way to get into literal backstory)
What was the last time they cried, and under what circumstances? (Good way to get some *emotional* backstory in.)
Are they an oldest, middle, youngest or only child? (This one might be a me thing, because I LOVE writing/reading about family dynamics, but knowing what kinds of things were ‘normal’ for them growing up is important.)
Describe the shoes they’re wearing. (This is a big catch all, gets into money, taste, practicality, level of wear, level of repair, literally what kind of shoes they require to live their life.)
Describe the place where they sleep. (ie what does their safe space look like. How much (or how little) care / decoration / personal touch goes into it.)
What is their favorite holiday? (How do they relate to their culture/outside world. Also fun is least favorite holiday.)
What objects do they always carry around with them? (What do they need for their normal, day-to-day routine? What does ‘normal’ even look like for them.)
Tips for creative writers who want to write about fantasy:
1. Build a rich and immersive world: Create a detailed and imaginative fantasy world with its own history, geography, cultures, and magical systems. Consider the rules and limitations of your world's magic to ensure consistency.
2. Develop unique and compelling characters: Craft memorable characters with distinct personalities, strengths, flaws, and goals. Explore how their backgrounds and abilities shape their experiences and interactions within the fantasy realm.
3. Weave in elements of magic and mythology: Introduce mythical creatures, mystical artifacts, and ancient legends into your storytelling. Use them to add depth, mystery, and wonder to your fantasy world.
4. Embrace world-building details: Pay attention to small but significant details in your world-building, such as food, clothing, customs, and languages. These details will enhance the believability and richness of your fantasy setting.
5. Create a compelling conflict: Develop an engaging conflict or quest that drives your story forward. This conflict could involve a battle between good and evil, a personal journey of self-discovery, or a struggle for power and redemption.
6. Blend familiar and unique elements: Combine familiar fantasy tropes with fresh and inventive ideas to create a unique reading experience. Balance the comfort of the familiar with the excitement of the unknown.
7. Use vivid and descriptive language: Paint a vivid picture with your words, using descriptive language to transport readers into your fantastical world. Engage all the senses to bring your settings, creatures, and magic to life.
8. Establish consistent rules and logic: While fantasy allows for imagination and magic, it's important to establish rules and logic within your world. This will ensure that readers can follow and invest in the story without feeling confused or disconnected.
9. Include themes and depth: Explore deeper themes and messages within your fantasy story. Address topics such as power, identity, morality, and the human condition to add layers of depth and resonance to your narrative.
10. Read widely in the fantasy genre: Immerse yourself in a variety of fantasy novels to familiarize yourself with different styles, world-building techniques, and storytelling approaches. Analyze what works and doesn't work for you as a reader and apply those insights to your own writing.
Remember, fantasy writing is an opportunity to unleash your imagination and transport readers to extraordinary realms. Have fun, be creative, and let your passion for the genre shine through in your storytelling.
Happy writing and happy adventures in the realm of fantasy!
Some quick tips for writing sexual tension in your novel:
1. Establish strong chemistry: Develop the characters' attraction to each other through meaningful interactions, shared interests, or a deep emotional connection. Their chemistry will lay the foundation for the sexual tension to build upon.
2. Use body language and non-verbal cues: Describe subtle gestures, lingering glances, or the way their bodies react in each other's presence. These non-verbal cues can heighten the tension and create a sense of anticipation.
3. Utilize dialogue: Employ flirty banter, double entendres, or suggestive remarks to create verbal sparring between characters. Clever wordplay can add layers of subtext and amplify the sexual tension.
4. Slow down the pace: Build tension by slowing down the pacing of scenes involving the characters. Emphasize their awareness of each other, the anticipation of physical contact, and the longing that grows with every passing moment.
5. Explore internal thoughts and desires: Give readers insight into the characters' internal dialogue, their secret desires, and the fantasies they have about each other. This adds depth and intensifies the sexual tension.
6. Employ the power of touch: Describe the impact of a brief brush of hands, accidental contact, or the lingering sensation left by a gentle touch. These tactile sensations can evoke a heightened sense of awareness and anticipation.
7. Create obstacles and conflicts: Introduce obstacles or conflicts that prevent the characters from acting upon their desires. These challenges can fuel the sexual tension, making the eventual release even more satisfying for both the characters and the readers.
8. Use sensory details: Engage the readers' senses by describing scents, sounds, or textures associated with the characters' proximity or potential intimacy. Sensory details can intensify the atmosphere and enhance the readers' experience of the sexual tension.
9. Play with power dynamics: Explore power dynamics between characters, such as a power imbalance or a push-pull dynamic. This can create a magnetic pull and increase the sexual tension as the characters navigate their desires and boundaries.
10. Employ the element of surprise: Introduce unexpected moments or situations that catch the characters off guard and heighten the sexual tension. These surprises can lead to spontaneous or forbidden encounters, increasing the anticipation and desire.
Remember to balance the sexual tension with the overall tone and genre of your novel, ensuring it aligns with your intended audience and fits organically within the story. With these tips, you'll be able to craft captivating scenes that sizzle with sexual tension, leaving readers eagerly turning the pages for more.
Happy writing!
Character Movements (Lips) Part 2
1. Smiling: The character's lips curl upwards at the corners, indicating happiness, friendliness, or amusement.
2. Frowning: The character's lips turn downwards, indicating sadness, displeasure, or concern.
3. Pouting: The character pushes their lower lip forward, often conveying disappointment, sulking, or a desire for attention.
4. Biting lip: The character lightly bites or presses their lips together, suggesting nervousness, anticipation, or hesitation.
5. Licking lips: The character's tongue briefly touches or moves across their lips, indicating desire, anticipation, or hunger.
6. Pressing lips together: The character's lips are firmly pressed together, indicating determination, frustration, or holding back emotions.
7. Parting lips: The character's lips slightly separate, often indicating surprise, shock, or readiness to speak.
8. Trembling lips: The character's lips quiver or shake, suggesting fear, anxiety, or suppressed emotions.
9. Whispering: The character's lips move closer together, and their voice becomes softer, indicating secrecy, confidentiality, or intimacy.
10. Mouthing words: The character moves their lips without making any sound, often used to convey silent communication or frustration.
Fantasy Guide to A Great House (19th-20th Century) - Anatomy of the House

When we think of the Victorians, the grand old Gilded Age or the Edwardians, we all think of those big mansions and manors where some of our favourite stories take place. But what did a great house look like?
Layout

All great houses are different and some, being built in different eras, may adhere to different styles. But the layout of certain rooms usually stayed somewhat the same.
The highest floors including the attic were reserved the children's rooms/nursery and the servants quarters.
The next floor would be reserved for bedrooms. On the first/ground floor, there will be the dining room, drawing room, library etc.
The basement/cellar would be where the kitchens and other food related rooms would be. Servants halls and boot rooms may also be down here too along scullery, where sometimes a maid would clean.
Rooms used by Servants

Boot Room: The Boot Room is where the valets, ladies maids, hallboys and sometimes footmen clean off shoes and certain items of clothing.
Kitchen: The Kitchen was usually either in the basement or the first floor of the house, connected to a garden where the house's vegetables were grown.
Butler's Pantry: A butler's pantry was where the serving items are stored. This is where the silver is cleaned, stored and counted. The butler would keep the wine log and other account books here. The butler and footmen would use this room.
Pantry: The Pantry would be connected to the kitchen. It is a room where the kitchens stock (food and beverages) would be kept.
Larder: The larder was cool area in the kitchen or a room connected to it where food is stored. Raw meat was often left here before cooking but pastry, milk, cooked meat, bread and butter can also be stored here.
Servants Hall: The Servant's Hall was where the staff ate their meals and spent their down time. They would write letters, take tea, sew and darn clothes. The servants Hall would usually have a fireplace, a large table for meals, be where the servant's cutlery and plates would be kept and where the bell board hung. (these bells were the way servants where summoned)
Wine Cellar: The wine cellar was where the wine was melt, usually in the basement. Only the butler would be permitted down there and everything would be catalogued by him too.
Butler's/Housekeeper's sitting rooms: In some houses, both the butler and the housekeeper had sitting rooms/offices downstairs. This was were they held meetings with staff, took their tea and dealt with accounts.
Scullery: The scullery was were the cleaning equipment was cleaned and stored. The scullery may even also double as a bedroom for the scullery maid.
Servery: The Servery connected to the dinning room. It was where the wine was left before the butler carried it out to be served. Some of the food would be delivered here to be carried out as well.
Servant's Sleeping Quarters: All servants excepting perhaps the kitchen maid and outside staff slept in the attics. Men and unmarried women would be kept at seperate sides of the house with the interconnecting doors locked and bolted every night by the butler and housekeeper. If the quarters were small, some servants may have to share rooms. Servants' bathrooms and washrooms would also be up there, supplied with hot water from the kitchens.
Rooms used by the Family

Dining room: The dining room was where the family ate their breakfast, lunch and dinner. It was also where the gentlemen took their after dinner drink before joking the ladies in the drawing room.
Drawing room: The Drawing Room was sort of a living/sitting room. It was mainly used in the evenings after dinner where the ladies would take their tea and coffee before being joined by the men. It could also be used for tea by the ladies during the day. The drawing room was seen as more of a women's room but any of the family could use it. The drawing room was a formal room but could also be used for more casual activities.
Library: The library is of course where the books are kept. The family would use this room for writing letters, reading, doing business with tenants and taking tea in the afternoons.
Bedrooms: The bedrooms would take up most of the upper floors. The unmarried women would sleep in one wing with bachelors at the furthest wing away. Married couples often had adjoining rooms with their own bedrooms in each and equipped with a boudoir or a sitting room.
Nursery: Was where the children slept, usually all together until old enough to move into bedrooms. They would be attended to be nannies and nursemaids round the clock.
Study: The study was a sort of home office where family could do paperwork, chill and write letters.
Dressing room: Dressing Rooms where usually attached to bedrooms where the family would be dressed and their clothes would be stored. The valets and ladies maids would have control of the room.
Hall: The hall was where large parties would gather for dancing or music or to be greeted before parties.
Furnishings and Decor

Most of these Great Houses were inherited which means, they came with a lot of other people's crap. Ornaments from anniversaries, paintings bought on holiday, furniture picked out by newly weds, all of it comes with the house. So most of the time everything seems rather cluttered.
As for Servant's Quarters, most of the furnishings may have been donated by the family as gifts. Most servants' halls would have a portrait of the sovereign or sometimes a religious figure to install a sense of morality into them.
Fantasy Guide to Royal Households and How they Work

When I say Households, I mean the entourage that follows around the royal family. The household went everywhere with them to care for their needs from the people who would empty their chamber pots to their noble companions. Most royal households are basically the same as noble ones, only on grander scale. Every royal had a household and an entourage as well as every noble at court.
Palace Personnel ~ The Commons

The commons were an intregal part of every household. They made up perhaps 80% of the work force. Royal courts were often on the road and never spent more than a few months at every palace. The court was constantly moving. Some positions were not permanent, meaning certain servants did not travel with the court because they were employed at the palace only. They would be paid by the Monarch's paymaster.
Scullion: The scullion was a relatively easy position to fill so they were often changed as the court went from palace to palace. They would be responsible for scrubbing and cleaning the servants quarters and the kitchens. They would scrub floors with lye, scour pots with sand, sweep put the fireplace and clean up after the other servants. They were the first to rise in a castle and tasked to light all the fires in the kitchens. Scullions would just be employed to the palace and serve a multitude of chambers
Laundress: The laundress was responsible for the cleaning of anything made of fabric in the household. Since they are handling unmentionables, they knew what happened behind closed bedchamber doors. They knew when the King visited the Queen or hadn't, they knew when marriages were consummated or not and they knew when the Queen and royal women were not pregnant. They often sold secrets to pad their pockets. Laundresses might be permanent staff but sometimes not.
Minstrels: The minstrel was a commoner hired to play an instrument or sing for the entertainment of the royal. A royal might staff a few at a time but they would always have one on hand. The minstrel would likely come with their masters as they travelled. The minstrel might serve the main royal household but a royal might retain their own.
Cook: The cook was one of the most important servants in the household. They would have the task of overseeing the running of the kitchens and keeping supplies in order. They would likely be on call at all times. Henry VIII's cook was often woken in the night because his royal master wanted a midnight snack. The cook was a valued member of the household and would have been highly sought after if they were a very skilled cook. They would have travelled with the joint. Cooks were apart of the greater royal household but often royals retained private cooks for their own use.
Maidservant: The maidservant cleans the castle. She would sweep the floors, scrub them, empty the chamberpots, get rid of the ashes from the fire and ready the fire for later. She would make up the bed or strip it for the laundresses. She would wash anything that needed washing including furniture and ornaments. She was likely not a travelling servant and would be strictly employed at a single palace.
Jester: The jester was the hired entertainer. Working under the master of revels, the jester had the daunting task of making the monarch and their family laugh. They would tell jokes, tell stories, cause havoc in the court for laughs and lighten the mood. The most successful jester of all time was Will Somers, jester to Henry VIII. Will broke bad news to the infamously bad tempered monarch and got away with things that would have sent others to the block. Will survived most of Henry's reign, his head intact. Jesters would be apart of the main household though each royal might have one of their own.
Positions within the Royal Household ~ Noble


Nobility were always welcomed at court. They eat at court, slept at court and were cared for by the monarch. Some nobles had to sing for their supper and most were hired as royal servants. They weren't exactly scrubbing floors and would be paid handsomely with land that would generate wealth for them
The Steward/Seneschal: This person was the head of the royal's staff. They would have the task of running the lands and servants their master or mistress. The steward served as a backup and assistant in all the tasks even representing their master or mistress when they were unavailable. Would be a high ranking noble. Each royal household would have them.
Treasurer of the Household: The treasurer was the accountant and pay master. They would be in charge of ensuring debts were settled, wages were paid and the household was running within the budget. This was a coveted position because it gave the treasurer insight into the financial situations of the royals. Such info was wroth its weight in gold. Each royal would have one.
Usher: The Gentleman Usher would be in charge of escorting guests into the royal chambers and into the royal presence. They would act as a go between their royal master/mistress and the guest often going back and forth with messages. It was just as coveted as the position of chamberlain but with less responsibilities.
Master of Horse: The Master of Horse was in charge of seeing to the horses of their master. They would oversee the grooms or the stableboy/hands who were employed at the stables to actually care for the horses. The master of horse would ensure that the stables were in order and the horses were up to parr in order to bear royalty across the kingdom. Each royal would have one but there would a main one who acted as overseer.
Master of the Wardrobe/Mistress of the Robes: These are the nobility who are employed to look after the clothes of the royal they serve. This would mainly involve a managerial position, overseeing the inventory of the royal wardrobe (a warehouse like building that housed the clothing) and placing orders for new clothes. It was a tidy job that rarely involved getting the hands dirty. Each royal would have one.
Chamberlain/Valet: The chamberlain is employed to look after the Lord's bedchamber. This was the most sought out position as they effectively were the gateway into the royal presence. Their main task was making sure their boss was comfortable and happy. Could be a well born commoner or a noble. Each royal would have one.
The Page: All royal households had pages. They would be a young noble boy about seven years old sent to their royal master. He would be in charge of tidying up after the lord, carrying messages to other servants and occupants of the castle and serving him at meals. Unlike others on the list, the page would not be paid. His experience was his payment as he would learn the running of a court and how to be courtier. Each royal would have one.
Squires: Squires were like pages though they only served the men. They would accompany their royal master to battle, look after his armour and mail, ensure that his lord's horse was saddled, caring for their master's weapons. The squire would always be a young nobleman on the cusp of becoming a knight.
Governess: The governess is a noblewoman woman employed to oversee the Monarch's children's household. She would be the first teacher a royal child would have and would oversee the nursemaids who would have care of the physical person of the child. She would be appointed when the child was four or five. Notable governesses include Katherine Swynford (wife of John of Gaunt and mother to the Beaufort line), Margaret Pole (wife of Tudor Loyal Sir Richard Pole, sister of the last York heir Edward of Warwick, daughter of George Duke of Clarence and niece to King Edward VI and Richard III), Kat Ashley, Margaret Bryan, Madame de Maintenon and Baroness Lehzen. Most unmarried Princesses retained their governesses while Princes generally outgrew their governesses after they were breeched.
Gentlemen of the Privy Chamber: They were the male companions of a King or Prince, sort of like ladies in waiting but manly. They would accompany the King or Prince everywhere they would go and shared duties with Groom of the Stool (royal toilet paper dispenser) and the Chief Gentleman of the Chamber (overseeing the staff and maintaining the chamber). They would help their master get ready, serve him at the table and organize hunting and games to keep him entertained. Gentlemen and companions where often chosen for their connections as well as their master's own opinion. Henry VIII's gentlemen included: Sir William Compton (ward of Henry VII and heir to rich lands), Sir Henry Norris (the grandson of William Norris who fought with Henry's father at Stroke and a relation to the Yorkists Lovells), Sir Anthony Denny (son of Sir Edmund Denny Baron of the Exchequer) Sir Michael Stanhope (brother in law to Edward Seymour, Duke of Somerset), Charles Brandon (ward of Henry VII and son of Tudor Loyalists)
Ladies in Waiting and Maids in Waiting or Maids of Honour: These are the female attendants to the Queen or Princess. Ladies in Waiting were married while the Maids were unmarried. They would have to attend their mistress wherever she went, help her get ready, keep her chambers in order, write letters for the Queen and maintaining her honour. They were chosen for their connections. Using Katherine of Aragon as an example, her Ladies in Waiting included: Maria de Salinas (daughter of Juan Sancriz de Salinas secretary to Isabella, Princess of Portugal and a Spanish courtier in the service to Katherine's parents, wife of Baron Willoughby de Ersby), Elizabeth Howard (the daughter of Thomas Howard, 2nd Duke of Norfolk, sister to Thomas Howard, 3rd Duke of Norfolk and wife to Thomas Boleyn, ambassador to France), Anne Hastings (daughter of William Hastings, 1st Baron Hastings, wife to George Talbot, Earl of Shrewsbury and Lord Steward.), Agnes Tilney (wife to Thomas Howard, Earl of and 2nd Duke of Norfolk.), Elizabeth Scrope (wife of John de Vere, Earl of Oxford, a loyal Tudor lord), Margaret Scrope (wife of Sir Edmund de la Pole, Earl of Suffolk cousin to the King), Anne Stafford (sister of the Duke of Buckingham, married Sir George Hastings, Earl of Huntington and daughter of Henry Stafford, 2nd Duke of Buckingham (cousin to the King) and Lady Katherine Woodville (sister of King Henry VIII's grandmother and his great aunt by her marriage), Elizabeth Stafford (sister to Anne Stafford wife Robert Radcliffe, Lord Fitzwalter and Earl of Sussex around). Their connections are what got them their places and you can see why they were chosen.
Accommodation
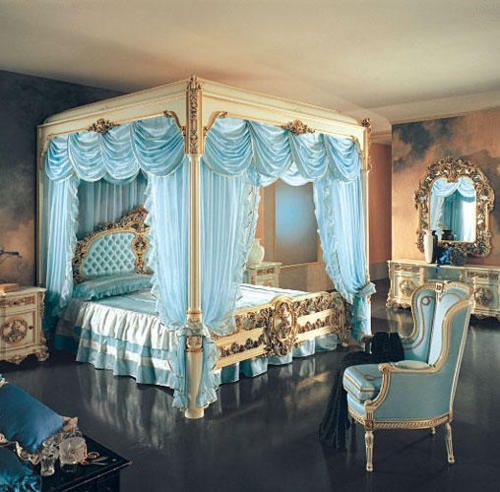

Accommodation can be a difficult thing to sort both as a writer and a steward. You might have a palace of 200+ bedchambers in which you must house a staff of 500-/+, a varying amount of nobles, the royal family (of a varying amount) and their own households. When assigning rooms it is best to think of a Russian nesting doll. Start from the inside and work your way to the outside.
The best rooms go to the monarch, their consort and their children/siblings/parent(s). These chambers would include the bedroom, a drawing room/ common area, a privy, a closet (a small chamber that can be used for prayer or work). They would be furnished with the best cloth, the best candles and whatever furniture brought by the resident since most royal courts travelled from palace to palace. They will also have chambers for their personal servants such as ladies in waiting and grooms.
The second best set of rooms would go to the highest ranking nobles/people in the court. These rooms would be less fancy and a little smaller. These would be given to from titled nobility descending from those of Ducal rank (Dukes/Duchesses) or even members of the council such as Thomas Cromwell in Tudor times.
The next set would be considerably smaller, perhaps minus a closet or a drawing room. Given to lower nobility.
The next level of chambers would be smaller perhaps only the bedroom and a common area given to minor nobles.
The last set of rooms would be small and only hold enough room for a bedroom. Servants would have to sleep on the ground on pallets beside their masters.
Any other guests at court would have to stay at off-site locations around the palace in the city. Some nobles at houses around major palaces just in case they arrived late or were kicked out of court.
-
 the-flower32 liked this · 1 week ago
the-flower32 liked this · 1 week ago -
 rockonfishboy liked this · 3 weeks ago
rockonfishboy liked this · 3 weeks ago -
 caspertacoguy liked this · 2 months ago
caspertacoguy liked this · 2 months ago -
 babydeershark liked this · 3 months ago
babydeershark liked this · 3 months ago -
 darkfunstarlight liked this · 3 months ago
darkfunstarlight liked this · 3 months ago -
 evansclcver reblogged this · 3 months ago
evansclcver reblogged this · 3 months ago -
 rosewritingfridge reblogged this · 4 months ago
rosewritingfridge reblogged this · 4 months ago -
 horrorfevers liked this · 4 months ago
horrorfevers liked this · 4 months ago -
 horrorived liked this · 5 months ago
horrorived liked this · 5 months ago -
 the-moons-coffin liked this · 5 months ago
the-moons-coffin liked this · 5 months ago -
 sumflowerd liked this · 5 months ago
sumflowerd liked this · 5 months ago -
 asayyun14 liked this · 5 months ago
asayyun14 liked this · 5 months ago -
 wynters-writings liked this · 5 months ago
wynters-writings liked this · 5 months ago -
 helplessromantical liked this · 5 months ago
helplessromantical liked this · 5 months ago -
 ayeshite liked this · 5 months ago
ayeshite liked this · 5 months ago -
 lactariusindigo reblogged this · 5 months ago
lactariusindigo reblogged this · 5 months ago -
 sherlocksittinginthelittlecouch liked this · 6 months ago
sherlocksittinginthelittlecouch liked this · 6 months ago -
 wowdragonhead liked this · 6 months ago
wowdragonhead liked this · 6 months ago -
 luckyicekitsune liked this · 6 months ago
luckyicekitsune liked this · 6 months ago -
 danaburrsir liked this · 6 months ago
danaburrsir liked this · 6 months ago -
 thetwistedarchives reblogged this · 6 months ago
thetwistedarchives reblogged this · 6 months ago -
 stxrlight09 liked this · 6 months ago
stxrlight09 liked this · 6 months ago -
 turtlefan625 liked this · 6 months ago
turtlefan625 liked this · 6 months ago -
 a6surdist liked this · 6 months ago
a6surdist liked this · 6 months ago -
 bubblelockerwhitter liked this · 6 months ago
bubblelockerwhitter liked this · 6 months ago -
 broekenwing04 liked this · 6 months ago
broekenwing04 liked this · 6 months ago -
 infernalcharm liked this · 7 months ago
infernalcharm liked this · 7 months ago -
 bluenightpicture reblogged this · 7 months ago
bluenightpicture reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 c4tharsys reblogged this · 7 months ago
c4tharsys reblogged this · 7 months ago -
 c4tharsys liked this · 7 months ago
c4tharsys liked this · 7 months ago -
 celestiasoloria liked this · 7 months ago
celestiasoloria liked this · 7 months ago -
 skylarcl liked this · 8 months ago
skylarcl liked this · 8 months ago -
 colpadack reblogged this · 8 months ago
colpadack reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 moreninafk liked this · 8 months ago
moreninafk liked this · 8 months ago -
 nuffsaidd liked this · 8 months ago
nuffsaidd liked this · 8 months ago -
 therepear13 liked this · 8 months ago
therepear13 liked this · 8 months ago -
 esmeray-nyx liked this · 8 months ago
esmeray-nyx liked this · 8 months ago -
 bluenightpicture reblogged this · 8 months ago
bluenightpicture reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 xavilly liked this · 8 months ago
xavilly liked this · 8 months ago -
 playerofthedawn liked this · 8 months ago
playerofthedawn liked this · 8 months ago -
 sweet-cuddlebug liked this · 8 months ago
sweet-cuddlebug liked this · 8 months ago -
 auroraescritora liked this · 8 months ago
auroraescritora liked this · 8 months ago -
 the-penguin-of-baskervilles liked this · 8 months ago
the-penguin-of-baskervilles liked this · 8 months ago -
 onceuponabloom liked this · 8 months ago
onceuponabloom liked this · 8 months ago -
 evanthesence liked this · 8 months ago
evanthesence liked this · 8 months ago -
 snixkerball liked this · 8 months ago
snixkerball liked this · 8 months ago -
 build-a-problem-musical reblogged this · 8 months ago
build-a-problem-musical reblogged this · 8 months ago -
 coravall01 liked this · 8 months ago
coravall01 liked this · 8 months ago
